What is Kinesis?
Kinesis re-creates Sound Money for the 21st Century. Conceptually it’s vaulted gold and silver that’s digitized and deliverable in any quantity by the implementation of a blockchain.
The nation of Indonesia (the fourth largest country in the world by population) rolled this out as a payment and savings solution in August of 2023, and more public-private partnerships are on the way.
Expand the following sections for background concepts:
The Case for Sound Money: Stability, Trust, and Economic Freedom
As our world becomes increasingly complex and interconnected, the necessity for a reliable form of currency has never been greater. Yet, the basic tenets of money—durability, divisibility, and a stable store of value—are being eroded by unchecked money-printing and inflation. This is where the time-honored concept of sound money comes in.
Limited Supply: A Shield Against Inflation
Inflation is the silent thief that erodes the buying power of your hard-earned money. When governments have the ability to print money indiscriminately, each unit of currency loses its value, impacting your purchasing power. Sound money, characterized by its limited or fixed supply, acts as a shield against this dilution of value.
A Reliable Store of Value
Imagine saving for years, only to discover that your savings can’t buy you what they once could. Sound money addresses this by providing a consistent store of value. It doesn’t decay or spoil, and its intrinsic value remains relatively stable over time. This is crucial for long-term financial planning and wealth accumulation.
Possibly the best way to visualize this is with this chart of historical gold prices from GoldMoney.com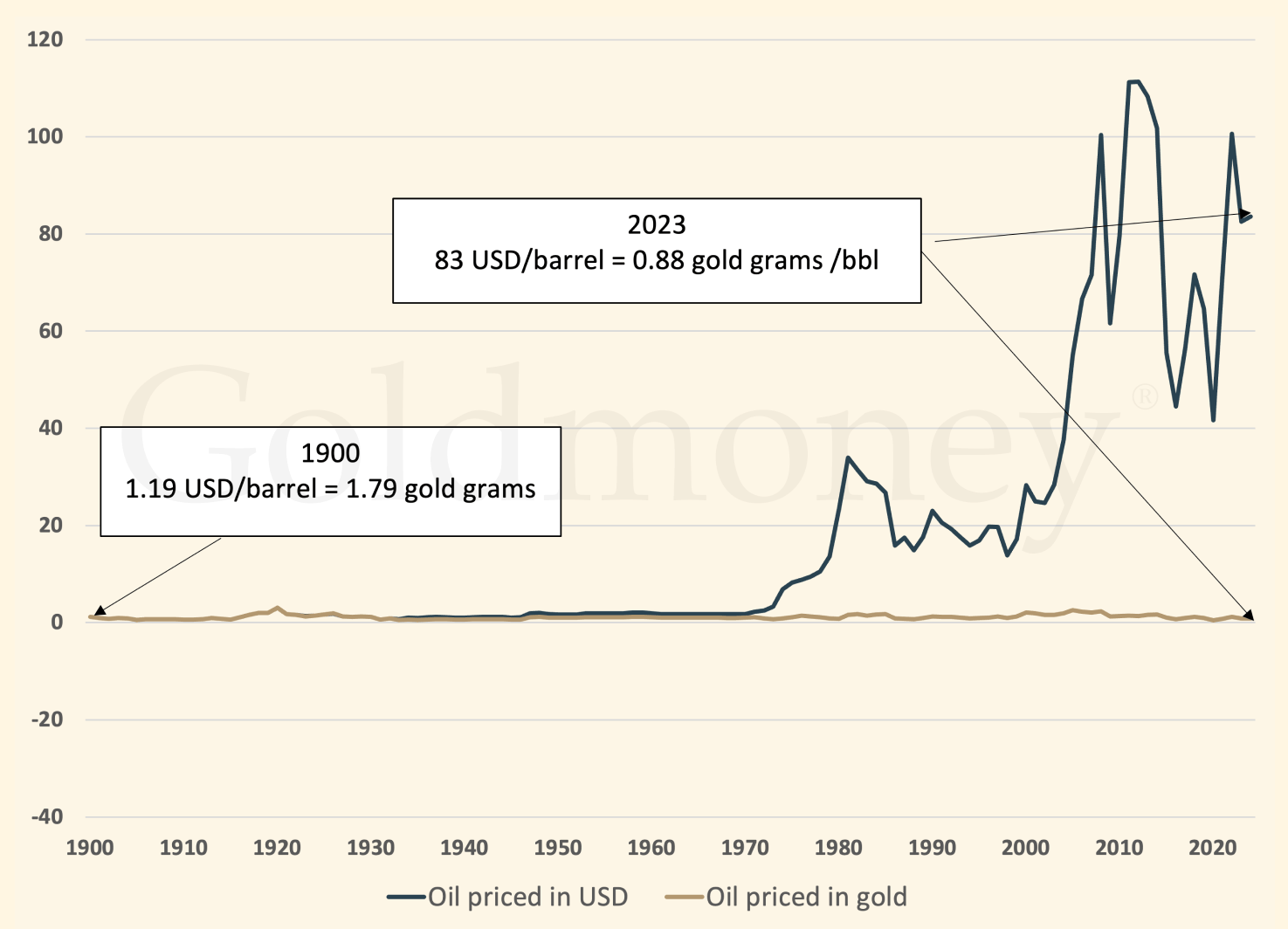
Divisibility: Practical for Everyday Use
What good is a currency if it’s not practical for everyday transactions? Sound money is easily divisible into smaller units without losing its value. This flexibility makes it ideal for both large-scale investments and small, daily transactions.
Trust and Transparency
Sound money has built-in features that foster trust. Its limited supply and enduring value mean that people can trust it to serve its primary functions as a medium of exchange and a store of value. Additionally, the transparent rules surrounding sound money minimize the risk of manipulation, further enhancing its reliability.
Conclusion
In a time of economic uncertainty and fiscal irresponsibility, the importance of sound money cannot be overstated. It offers stability, encourages trust, and provides a solid foundation for the economic freedom of individuals and nations alike. By embracing the principles of sound money, we arm ourselves against the erosive effects of inflation and secure a more prosperous future for all.
At its core, a blockchain is a digital ledger or record-keeping system. But instead of being stored in one place like a traditional database, this ledger is distributed across multiple computers, known as nodes, around the world. Each of these nodes has a complete or partial copy of the blockchain, and they work together to maintain and update this ledger.
Imagine a blockchain as a series of digital “blocks” that contain lists of transactions. Each time a transaction is made, it’s verified by the nodes in the network and then added to a new block. This new block is linked to the previous one, forming a chain of blocks—hence the name “blockchain.”
The unique thing about blockchain is its decentralization. Unlike conventional databases managed by a central authority, like a bank or government, a blockchain is maintained collectively by the nodes. This makes the system more transparent and secure because no single entity has complete control over the entire blockchain. It’s also more difficult to tamper with: to change one block, you’d need to change every block that comes after it, which would require the consensus of the majority of nodes—a practically impossible task.
One more crucial feature is that once a block has been added to the blockchain, it can’t be changed or removed. This makes the blockchain a tamper-proof, “immutable” record of all transactions that have ever occurred on that network.
In summary, a blockchain is a decentralized, transparent, and immutable digital ledger, maintained by a network of nodes. It serves as the foundational technology for various applications, from cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Kinesis to more complex systems for supply chain management, digital voting, and beyond.
So? What's so special about this?
Well, there are a few things that I think are genius about the way Kinesis went about trying to re-create money:
Blockchains are high trust. Once a transaction is added to the blockchain, it’s there permanently. When I pay you in Kinesis you know the payment is irrevocable, unlike a check or credit card transaction.
It’s also visible. Unlike a bank, or a gold vaulting service where they have an internal database that tracks ownership of assets, a blockchain is outward facing and visible to the world. The ownership of every gram of metal in the vaults, and every transfer is visible in a mostly anonymized way. You can see this on the official Kinesis Explorer, or on the open-source watcher node I run here.
Gold and Silver are unmatched in their ability to preserve purchasing power
Gold and silver have done this since the beginning of history.Nothing is a better, more proven store of value.
All the metal in the Kinesis vaults is owned by the users
With a bank, when you deposit money it no longer is yours – instead, it becomes an unsecured liability of the bank. Kinesis, on the other hand, acts as a bailee for your metal. Should something happen to Kinesis, your metal remains yours and can’t be seized as one of Kinesis’ assets. Because it’s your asset.
All the metal is audited by then internationally respected auditor every quarter
You know your metal is still there, vaulted and insured, because Inspectorate (Bureau Veritas) inspected, tested, and weighed it within the last 3 months.
Blockchain means you can spend gold or silver in arbitrary amounts, in seconds.
In Kinesis, the units of account are KAU (representing a gram of gold, currently worth a bit more than $60) and KAG (which is an ounce of silver – about $25 each.) If, however, you want to spend 23¢ you can do that because KAU and KAG are divisible down to tiny fractions. As I type this, 25¢ is 0.00401 KAU, and I can send that to you anywhere in the world in about 3 seconds.
You can spend your gold and silver on a debit card
This is true most places. The United States has been a bit authoritarian about alternative payment methods rolling out, but users in 62 countries so far have access to a debit card that allows them to spend Kinesis anywhere that accepts MasterCard. The conversion from metal to local currency happens at the point of sale, and is immediate and painless.
In Kinesis your metal earns a yield and has free storage
This sounds impossible, but it’s not. You’ll need to read on a bit more for the explanation of how this works, though.